As federal agencies prepare to deregulate transgenic chestnuts, Indigenous nations assert right to access and care for them
As federal agencies prepare to deregulate transgenic chestnuts, Indigenous nations assert right to access and care for them
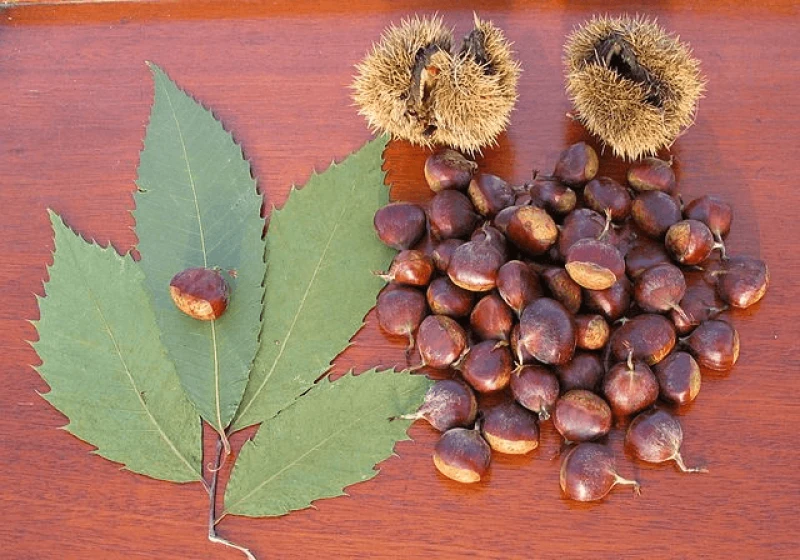


The American chestnut tree, or číhtkęr in Tuscarora, once grew across what is currently the eastern United States, from Mississippi to Georgia, and into southeastern Canada. The beloved and ecologically important species was harvested by Indigenous peoples for millennia and once numbered in the billions, providing food and habitat to countless birds, insects, and mammals of eastern forests, before being wiped out by rampant logging and a deadly fungal blight brought on by European colonization.
Now, a transgenic version of the American chestnut that can withstand the blight is on the cusp of being deregulated by the U.S. government. (Transgenic organisms contain DNA from other species.) When that happens, people will be able to grow the blight-resistant trees without restriction. For years, controversy has swirled around the ethics of using novel biotechnology for species conservation. But [Neil] Patterson, who previously directed the Tuscarora Environment Program and today is the assistant director of the Center for Native Peoples and the Environment at the State University of New York’s College of Environmental Science and Forestry in Syracuse, has a different question: What good is bringing back a species without also restoring its traditional relationships with the Indigenous peoples who helped it flourish?
This is an excerpt. Read the original post here

 | Videos | More... |

Video: Nuclear energy will destroy us? Global warming is an existential threat? Chemicals are massacring bees? Donate to the Green Industrial Complex!
 | Bees & Pollinators | More... |

GLP podcast: Science journalism is a mess. Here’s how to fix it

Mosquito massacre: Can we safely tackle malaria with a CRISPR gene drive?

Are we facing an ‘Insect Apocalypse’ caused by ‘intensive, industrial’ farming and agricultural chemicals? The media say yes; Science says ‘no’
 | Infographics | More... |

Infographic: Global regulatory and health research agencies on whether glyphosate causes cancer
 | GMO FAQs | More... |

Why is there controversy over GMO foods but not GMO drugs?

How are GMOs labeled around the world?

How does genetic engineering differ from conventional breeding?
 | GLP Profiles | More... |

Alex Jones: Right-wing conspiracy theorist stokes fear of GMOs, pesticides to sell ‘health supplements’




 Viewpoint — Fact checking MAHA mythmakers: How wellness influencers and RFK, Jr. undermine American science and health
Viewpoint — Fact checking MAHA mythmakers: How wellness influencers and RFK, Jr. undermine American science and health Viewpoint: Video — Big Solar is gobbling up productive agricultural land and hurting farmers yet providing little energy or sustainabilty gains
Viewpoint: Video — Big Solar is gobbling up productive agricultural land and hurting farmers yet providing little energy or sustainabilty gains Fighting deforestation with CO2: Biotechnology breakthrough creates sustainable palm oil alternative for cosmetics
Fighting deforestation with CO2: Biotechnology breakthrough creates sustainable palm oil alternative for cosmetics Trust issues: What happens when therapists use ChatGPT?
Trust issues: What happens when therapists use ChatGPT? 30-year-old tomato line shows genetic resistance to devastating virus
30-year-old tomato line shows genetic resistance to devastating virus California, Washington, Oregon forge immunization alliance to safeguard vaccine access against federal undermining
California, Washington, Oregon forge immunization alliance to safeguard vaccine access against federal undermining The free-range chicken dilemma: Better for birds, but with substantial costs
The free-range chicken dilemma: Better for birds, but with substantial costs ‘You have to treat the brain first’: Rethinking chronic pain with Sanjay Gupta
‘You have to treat the brain first’: Rethinking chronic pain with Sanjay Gupta