Biofuels, e-fuels and solar fuels are possible substitutes for fossil fuels and electric vehicles. Is that realistic?
Biofuels, e-fuels and solar fuels are possible substitutes for fossil fuels and electric vehicles. Is that realistic?
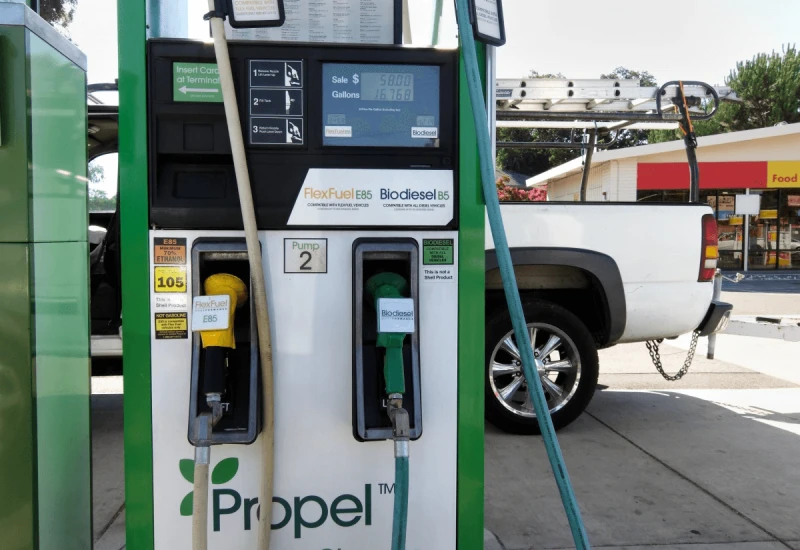


Synthetic fuels (or synfuels) are liquid or gaseous fuels that are practically similar to fossil fuels in everything but the way they’re produced. While conventional fossil fuels come from the process of organic matter being turned into coal, natural gas or oil, underground, over millions of years, synthetic fuels are produced artificially by replicating these natural processes, using renewable sources such as water, biomass, and carbon dioxide.
As the political demands for a carbon-neutral future (and mass electrification) get more persistent, many purists in the automotive industry keep clamoring for synthetic fuels to take over as a substitute for both fossil fuels and electric vehicles. Such is the case for Ferrari and Porsche, which are both heavily invested in e-fuels, a type of synfuel produced through electrolysis and seen as a suitable alternative to electric batteries. It is easy, at face value at least, to make a case for such an approach.
Under the present conditions, it seems rather unlikely that e-fuels can become cheap and abundant early enough to replace fossil fuels on a broad scale. The study published by the Nature Climate Change journal strongly asserts that e-fuels cannot override the “urgent need for broad electrification”, and deems them unlikely to help reach the 2030 climate target. However, the research paper also judges e-fuels as likely to become a competitive option as technological advancements help reduce their processing costs over the years.
This is an excerpt. Read the original post here

 | Videos | More... |

Video: Nuclear energy will destroy us? Global warming is an existential threat? Chemicals are massacring bees? Donate to the Green Industrial Complex!
 | Bees & Pollinators | More... |

GLP podcast: Science journalism is a mess. Here’s how to fix it

Mosquito massacre: Can we safely tackle malaria with a CRISPR gene drive?

Are we facing an ‘Insect Apocalypse’ caused by ‘intensive, industrial’ farming and agricultural chemicals? The media say yes; Science says ‘no’
 | Infographics | More... |

Infographic: Global regulatory and health research agencies on whether glyphosate causes cancer
 | GMO FAQs | More... |

Why is there controversy over GMO foods but not GMO drugs?

How are GMOs labeled around the world?

How does genetic engineering differ from conventional breeding?
 | GLP Profiles | More... |

Alex Jones: Right-wing conspiracy theorist stokes fear of GMOs, pesticides to sell ‘health supplements’




 Viewpoint — Fact checking MAHA mythmakers: How wellness influencers and RFK, Jr. undermine American science and health
Viewpoint — Fact checking MAHA mythmakers: How wellness influencers and RFK, Jr. undermine American science and health Viewpoint: Video — Big Solar is gobbling up productive agricultural land and hurting farmers yet providing little energy or sustainabilty gains
Viewpoint: Video — Big Solar is gobbling up productive agricultural land and hurting farmers yet providing little energy or sustainabilty gains Fighting deforestation with CO2: Biotechnology breakthrough creates sustainable palm oil alternative for cosmetics
Fighting deforestation with CO2: Biotechnology breakthrough creates sustainable palm oil alternative for cosmetics Trust issues: What happens when therapists use ChatGPT?
Trust issues: What happens when therapists use ChatGPT? 30-year-old tomato line shows genetic resistance to devastating virus
30-year-old tomato line shows genetic resistance to devastating virus California, Washington, Oregon forge immunization alliance to safeguard vaccine access against federal undermining
California, Washington, Oregon forge immunization alliance to safeguard vaccine access against federal undermining The free-range chicken dilemma: Better for birds, but with substantial costs
The free-range chicken dilemma: Better for birds, but with substantial costs ‘You have to treat the brain first’: Rethinking chronic pain with Sanjay Gupta
‘You have to treat the brain first’: Rethinking chronic pain with Sanjay Gupta