Low carb diet danger alert: It increases the risk of colorectal cancer
Low carb diet danger alert: It increases the risk of colorectal cancer
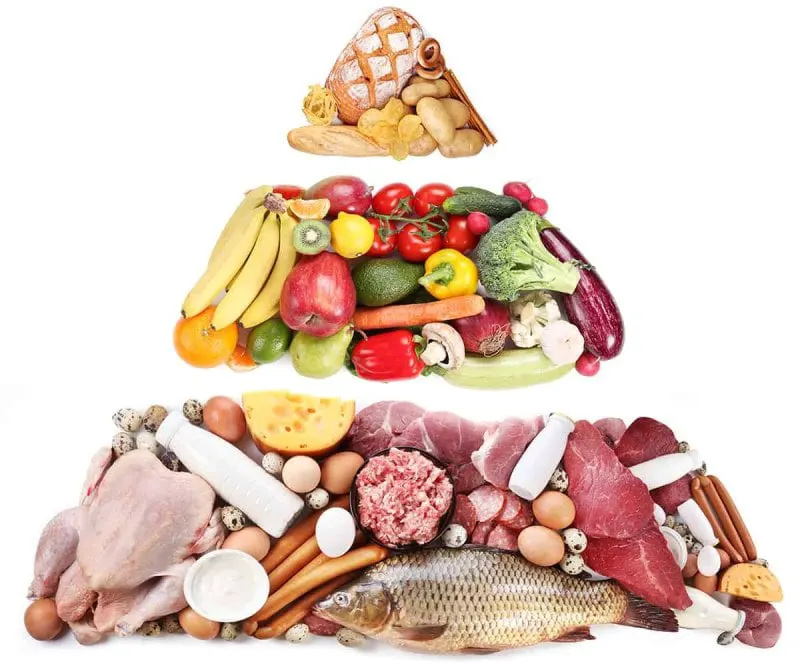


Researchers from the University of Toronto in Canada recently conducted a study to explore how low carb diets can affect bacteria linked to colorectal cancer.
Their study results showed that a type of Escherichia coli is negatively impacted by low carb diets. The scientists found that it increased the development of polyps. Some polyps have the potential to develop into colorectal cancer.
Overall, mice on low carb diets combined with E. coli experienced such disruption and damage to their gut microbiome that researchers found it to be an environment that promotes colorectal cancer.
As concerning as these results were, the researchers found that adding fiber to these mice’s diets reduced tumor formation and helped control inflammation.
The researchers want to continue this line of research by determining whether certain types of fiber are more protective and studying their effects on humans.
This is an excerpt. Read the original post here

 | Videos | More... |

Video: Nuclear energy will destroy us? Global warming is an existential threat? Chemicals are massacring bees? Donate to the Green Industrial Complex!
 | Bees & Pollinators | More... |

GLP podcast: Science journalism is a mess. Here’s how to fix it

Mosquito massacre: Can we safely tackle malaria with a CRISPR gene drive?

Are we facing an ‘Insect Apocalypse’ caused by ‘intensive, industrial’ farming and agricultural chemicals? The media say yes; Science says ‘no’
 | Infographics | More... |

Infographic: Global regulatory and health research agencies on whether glyphosate causes cancer
 | GMO FAQs | More... |

Why is there controversy over GMO foods but not GMO drugs?

How are GMOs labeled around the world?

How does genetic engineering differ from conventional breeding?
 | GLP Profiles | More... |

Alex Jones: Right-wing conspiracy theorist stokes fear of GMOs, pesticides to sell ‘health supplements’




 A single high dose of LSD can ease anxiety and depression for months
A single high dose of LSD can ease anxiety and depression for months From plastic coasters to human hearts: Inside the race to print the human body
From plastic coasters to human hearts: Inside the race to print the human body CRISPR pork: U.S. approves first gene-edited pigs for consumption
CRISPR pork: U.S. approves first gene-edited pigs for consumption Viewpoint: Life and death decisions: RFK, Jr.’s shady FDA “expert panels” operate in secret with no transcripts or conflict of interest reviews
Viewpoint: Life and death decisions: RFK, Jr.’s shady FDA “expert panels” operate in secret with no transcripts or conflict of interest reviews ‘SuperAgers’: Why some people have the brains and memory capacity of people decades younger
‘SuperAgers’: Why some people have the brains and memory capacity of people decades younger  Baby food panic, brought to you by trial lawyers hoping to prosecute by press release
Baby food panic, brought to you by trial lawyers hoping to prosecute by press release From ‘Frankenfood’ to superfood: Can the purple tomato overcome GMO myths to win over consumers?
From ‘Frankenfood’ to superfood: Can the purple tomato overcome GMO myths to win over consumers? When farmers deny science: The hypocrisy hurting agriculture’s credibility
When farmers deny science: The hypocrisy hurting agriculture’s credibility