Multi-country effort helps develop gene-edited rice that both boosts yield and resists disease
Multi-country effort helps develop gene-edited rice that both boosts yield and resists disease


Small-scale field trials in China showed that the newly created rice variety, developed through genome editing of a newly discovered gene, exhibited both high yields and resistance to the fungus that causes a serious disease called rice blast. Rice is an essential crop that feeds half of the world’s population.
Guotian Li, a co-lead author of the study, initially discovered a mutant known as a lesion mimic mutant while working as a postdoctoral scholar in Pamela Ronald’s lab at UC Davis. Ronald is co-lead author and Distinguished Professor in the Department of Plant Pathology and the Genome Center.
“It’s quite a step forward that his team was able to improve this gene, making it potentially useful for farmers. That makes it important,” Ronald said.
The roots of the discovery began in Ronald’s lab, where they created and sequenced 3,200 distinct rice strains, each possessing diverse mutations. Among these strains, Guotian identified one with dark patches on its leaves.

“He found that the strain was also resistant to bacterial infection, but it was extremely small and low yielding,” Ronald said. “These types of ‘lesion mimic’ mutants have been found before but only in a few cases have they been useful to farmers because of the low yield.”

Working with CRISPR
Guotian continued the research when he joined Huazhong Agricultural University in Wuhan, China.
His team used sequencing and other approaches to isolate the gene related to the mutation and used CRISPR-CAS9 genome editing to recreate the resistance trait, eventually identifying a line that had good yield and was resistant to three different pathogens, including the fungus that causes rice blast.
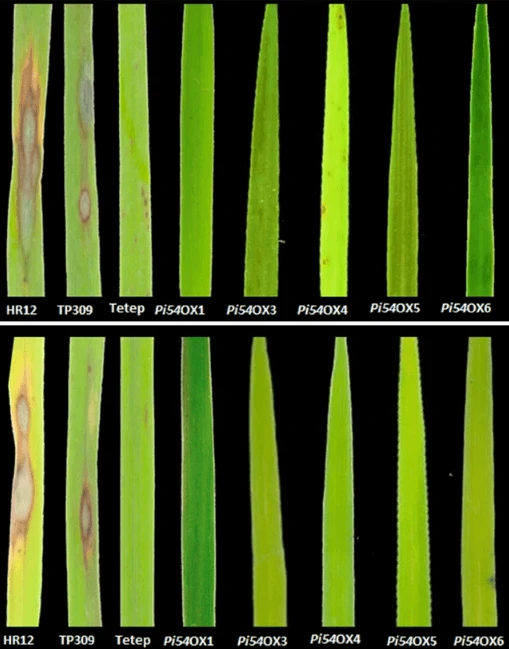

In small-scale field trials planted in disease-heavy plots, the new rice plants produced five times more yield than the control rice, which was damaged by the fungus, Ronald said.
“Blast is the most serious disease of plants in the world because it affects virtually all growing regions of rice and also because rice is a huge crop,” Ronald said.
Future applications
The researchers hope to recreate this mutation in commonly grown rice varieties. Currently they have only optimized this gene in a model variety called “Kitaake” that is not grown widely. They also hope to target the same gene in wheat to create disease-resistant wheat.
“A lot of these lesion mimic mutants have been discovered and sort of put aside because they have low yield. We’re hoping that people can go look at some of these and see if they can edit them to get a nice balance between resistance and high yield,” Ronald said.
Read the original post here

 | Videos | More... |

Video: Nuclear energy will destroy us? Global warming is an existential threat? Chemicals are massacring bees? Donate to the Green Industrial Complex!
 | Bees & Pollinators | More... |

GLP podcast: Science journalism is a mess. Here’s how to fix it

Mosquito massacre: Can we safely tackle malaria with a CRISPR gene drive?

Are we facing an ‘Insect Apocalypse’ caused by ‘intensive, industrial’ farming and agricultural chemicals? The media say yes; Science says ‘no’
 | Infographics | More... |

Infographic: Global regulatory and health research agencies on whether glyphosate causes cancer
 | GMO FAQs | More... |

Why is there controversy over GMO foods but not GMO drugs?

How are GMOs labeled around the world?

How does genetic engineering differ from conventional breeding?
 | GLP Profiles | More... |

Alex Jones: Right-wing conspiracy theorist stokes fear of GMOs, pesticides to sell ‘health supplements’




 Viewpoint — Fact checking MAHA mythmakers: How wellness influencers and RFK, Jr. undermine American science and health
Viewpoint — Fact checking MAHA mythmakers: How wellness influencers and RFK, Jr. undermine American science and health Viewpoint: Video — Big Solar is gobbling up productive agricultural land and hurting farmers yet providing little energy or sustainabilty gains
Viewpoint: Video — Big Solar is gobbling up productive agricultural land and hurting farmers yet providing little energy or sustainabilty gains Fighting deforestation with CO2: Biotechnology breakthrough creates sustainable palm oil alternative for cosmetics
Fighting deforestation with CO2: Biotechnology breakthrough creates sustainable palm oil alternative for cosmetics Trust issues: What happens when therapists use ChatGPT?
Trust issues: What happens when therapists use ChatGPT? California, Washington, Oregon forge immunization alliance to safeguard vaccine access against federal undermining
California, Washington, Oregon forge immunization alliance to safeguard vaccine access against federal undermining 30-year-old tomato line shows genetic resistance to devastating virus
30-year-old tomato line shows genetic resistance to devastating virus The free-range chicken dilemma: Better for birds, but with substantial costs
The free-range chicken dilemma: Better for birds, but with substantial costs ‘You have to treat the brain first’: Rethinking chronic pain with Sanjay Gupta
‘You have to treat the brain first’: Rethinking chronic pain with Sanjay Gupta