Viewpoint: Is our western food system based on ‘intensive agriculture’ broken? Not if the environment and alleviating poverty and hunger matter
Viewpoint: Is our western food system based on ‘intensive agriculture’ broken? Not if the environment and alleviating poverty and hunger matter
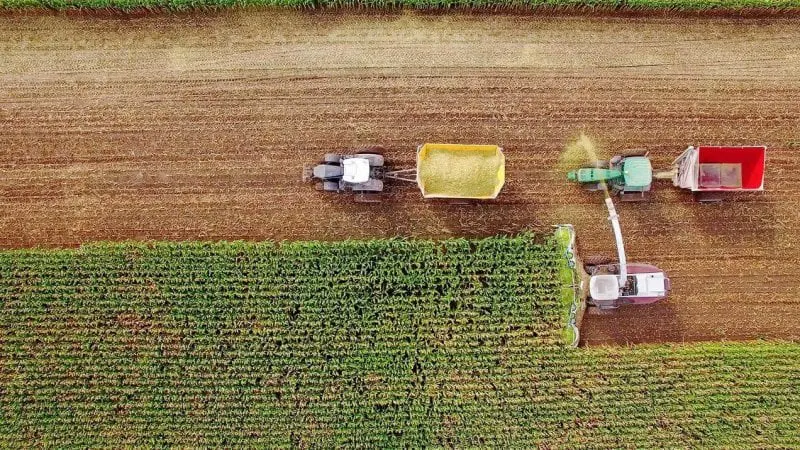

In the popular bourgeois imagination, the idealized farm looks something like the ones that sell produce at local farmers markets. But while small farms like these account for close to half of all U.S. farms, they produce less than 10 percent of total output.
The largest farms, by contrast, account for about 50 percent of output, relying on simplified production systems and economies of scale to feed a nation of 330 million people, vanishingly few of whom live anywhere near a farm or want to work in agriculture.
But U.S. dependence on large farms is not a conspiracy by big corporations. Without question, the U.S. food system has many problems. But persistent misperceptions about it, most especially among affluent consumers, are a function of its spectacular success, not its failure.
Any effort to address social and environmental problems associated with food production in the United States will need to first accommodate itself to the reality that, in a modern and affluent economy, the food system could not be anything other than large-scale, intensive, technological, and industrialized.
In reality, organic production accounts for little more than 1 percent of total U.S. agricultural land use. Meanwhile, only a bit more than 5 percent of food sales come from organic producers.
…
Because organic farming requires more land for every calorie or pound produced, a large-scale shift to organic farming would entail converting more forest and other land to farming, resulting in greater habitat loss and more greenhouse gas emissions. And while organic farming doesn’t use synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, it often results in greater nitrogen pollution because manure is a highly inefficient way to deliver nutrients to crops.
…
Ultimately, improving the U.S. food system will require, first, appreciating it for the social, economic, and technological marvel that it is. It feeds 330 million Americans and many millions more around the world.
Read the original post
 | Videos | More... |

Video: Nuclear energy will destroy us? Global warming is an existential threat? Chemicals are massacring bees? Donate to the Green Industrial Complex!
 | Bees & Pollinators | More... |

GLP podcast: Science journalism is a mess. Here’s how to fix it

Mosquito massacre: Can we safely tackle malaria with a CRISPR gene drive?

Are we facing an ‘Insect Apocalypse’ caused by ‘intensive, industrial’ farming and agricultural chemicals? The media say yes; Science says ‘no’
 | Infographics | More... |

Infographic: Global regulatory and health research agencies on whether glyphosate causes cancer
 | GMO FAQs | More... |

Why is there controversy over GMO foods but not GMO drugs?

How are GMOs labeled around the world?

How does genetic engineering differ from conventional breeding?
 | GLP Profiles | More... |

Alex Jones: Right-wing conspiracy theorist stokes fear of GMOs, pesticides to sell ‘health supplements’





 Trust issues: What happens when therapists use ChatGPT?
Trust issues: What happens when therapists use ChatGPT? California, Washington, Oregon forge immunization alliance to safeguard vaccine access against federal undermining
California, Washington, Oregon forge immunization alliance to safeguard vaccine access against federal undermining Fighting deforestation with CO2: Biotechnology breakthrough creates sustainable palm oil alternative for cosmetics
Fighting deforestation with CO2: Biotechnology breakthrough creates sustainable palm oil alternative for cosmetics Viewpoint — Fact checking MAHA mythmakers: How wellness influencers and RFK, Jr. undermine American science and health
Viewpoint — Fact checking MAHA mythmakers: How wellness influencers and RFK, Jr. undermine American science and health 30-year-old tomato line shows genetic resistance to devastating virus
30-year-old tomato line shows genetic resistance to devastating virus The free-range chicken dilemma: Better for birds, but with substantial costs
The free-range chicken dilemma: Better for birds, but with substantial costs Viewpoint: Video — Big Solar is gobbling up productive agricultural land and hurting farmers yet providing little energy or sustainabilty gains
Viewpoint: Video — Big Solar is gobbling up productive agricultural land and hurting farmers yet providing little energy or sustainabilty gains ‘You have to treat the brain first’:Rethinking chronic pain with Sanjay Gupta
‘You have to treat the brain first’:Rethinking chronic pain with Sanjay Gupta